Plane Waves at Interfaces
Purpose
Here, we provide theory for describing the behaviour of plane waves as they reach physical property interfaces. Reflection, refraction and transmission are discussed.
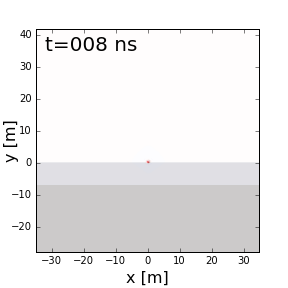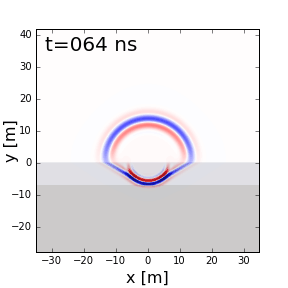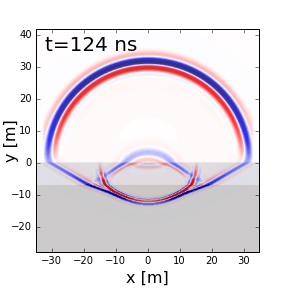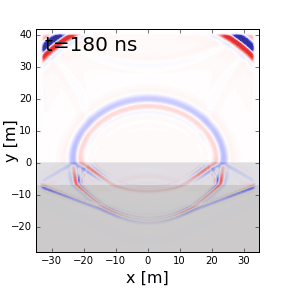
Fig. 57 Reflection, refraction and transmission of a ground penetrating radar signal.
Introduction
When EM waves reach an interface characterized by an abrupt change in physical properties, portions of the signal undergo reflection, refraction and transmission. In Fig. 57, we show these behaviours for a ground penetrating radar signal. A fundamental understanding of reflection, refraction and transmission can be obtained by considering plane waves. Here, we provide theory which describes the behaviour of plane waves as they interact with physical property interfaces. Numerical modeling apps are provided to simulate these behaviours.
Organization
The content within this portion is organized into 3 parts:
Reflection and Snell’s Law: Defines the relationship between the propagation directions of incident, reflected and refracted EM waves.
Fresnel Equations: Defines the relationships between the propagation directions and amplitudes of incident, reflected, refracted and transmitted EM waves.
N-Layer Earth: After characterizing the behaviours of plane waves at a single interface, we extend the theory to a layered Earth model.
Contents